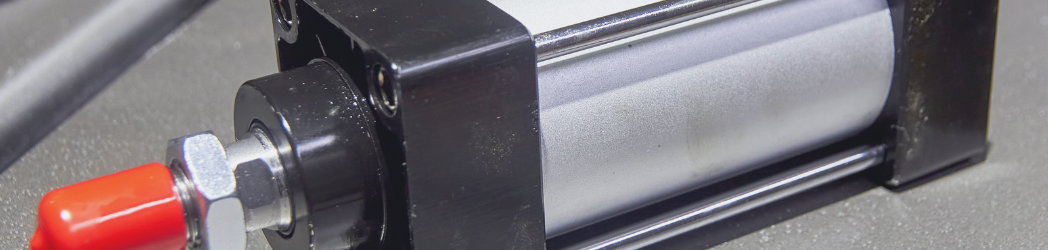
Hydraulic Cylinders: Frequently Asked Questions
The hydraulic cylinder is an essential component of hydraulic systems and is commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and transportation industries. Understanding the mechanics, materials, and maintenance of cylinders is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. In this blog post, we will answer some of the most common questions asked about hydraulic cylinders, including who invented them, how they work, how to maintain them, and much more.

Custom Hydraulic Cylinder Manufacturing near Grand Rapids, Michigan
Selecting the right hydraulic cylinder involves a thoughtful process to ensure it meets your specific needs. First and foremost, consider the load requirements. You’ll want to determine the maximum force the cylinder will need to exert, factoring in any potential variations or unexpected spikes. Next, assess the operating environment. Take note of factors like temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive substances, as these can impact the material and coating choices for the cylinder. Additionally, consider the stroke length, which is the distance the cylinder can extend and retract; it should comfortably accommodate the range of motion required for your application. Think about the mounting options available and how they align with your equipment. Finally, consult the manufacturer’s specifications and recommendations to ensure compatibility with your system and to guarantee a reliable and efficient performance.
The hydraulic cylinder was patented by Joseph Bramah in 1795 in England. Bramah was an English inventor and locksmith who used Blaise Pascals theory to create the hydraulic press. Pascal discovered in 1648 that applying pressure on a confined fluid exerted an equal force, and that pressure could be harnessed. Almost 100 years later Daniel Bernoulli used Pascals theory to pressurize water in pumps and mills. A few years after that it lead to Bramah’s invention which revolutionized the manufacturing industry and paved the way for modern hydraulic systems.
No, they cannot work with air. They are designed to work with hydraulic fluid, which is much denser than air and provides much more power. Air in the hydraulic system can cause a loss of pressure, which can lead to reduced performance or even system failure.
Yes, the size of a cylinder does matter. The size of the cylinder determines how much force it can generate and how much weight it can lift. Choosing the right size cylinder for your application is important for achieving optimal performance. Factors to consider when selecting a hydraulic cylinder include the application, operating conditions, and load capacity.
Yes, hydraulic cylinders can be repaired. Common repairs include replacing seals and repairing or replacing damaged parts. It is important to have your cylinders repaired by a qualified technician to ensure proper functioning. Regular maintenance can help prevent the need for major repairs and extend the life of your equipment.
Yes, hydraulic cylinders can become air locked. This can occur when air enters the system, preventing hydraulic fluid from flowing properly. Bleeding the system can help remove air and restore proper functioning. It is important to check the hydraulic system regularly for signs of airlock and address any issues promptly to prevent damage to the system.
Yes, your cylinders can be welded. However, it is important to use the proper welding techniques and materials to ensure the cylinder remains structurally sound. Welding should only be done by a qualified technician who has experience working with hydraulics.
Yes, you can bleed a hydraulic cylinder. Bleeding the system removes air and ensures proper functioning. The process involves opening the bleed valve to release any trapped air. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the correct tools when bleeding a hydraulic cylinder.
Yes, they can be cushioned. A hydraulic cushion is a feature in some hydraulic cylinders that helps to reduce the impact and shock caused by the cylinder’s motion. As the name states, It’s basically like a cushion for the cylinder, absorbing the energy created by the moving piston and slowing down its motion before it reaches the end of its stroke.
Hydraulic cushions are often used in applications where a heavy load is being lifted or moved, as they can help protect the load and the hydraulic system from damage. By providing a more controlled and gradual stop to the cylinder’s motion, hydraulic cushions can help to increase the safety and efficiency of hydraulic systems.
Various fluids can be used for hydraulic cylinders, including mineral-based oil, synthetic oil, and water-based fluids. The choice of fluid depends on the specific application and operating conditions. Factors to consider when selecting a hydraulic fluid include viscosity, temperature range, oxidation stability, and compatibility with seals and other system components. It is important to use a high-quality fluid that meets the manufacturer’s specifications and to perform regular fluid analysis and replacement to ensure optimal system performance and longevity.
Hydraulic cylinders are typically made of high-strength steel, although other materials such as aluminum and titanium may also be used. The cylinder barrel is usually made of seamless steel tubing, while the piston rod is made of high-strength steel and is often chrome plated for improved wear resistance. The end caps and other components may be made of steel or other materials depending on the specific application.
Drift is a common issue that occurs when the cylinder slowly moves or creeps even when the control valve is in the neutral position. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including worn seals, contamination, or improper adjustment of the control valve. Cylinder drift can be prevented by performing regular maintenance, such as replacing worn seals and cleaning the system, and by properly adjusting the control valve.
The bore is the inside diameter of the cylinder barrel, which houses the piston. The bore size determines the amount of force that the cylinder can generate and the size of the load it can lift. Bore sizes typically range from 1 inch to over 30 inches, with larger cylinders being used for heavy-duty applications.
No, cylinder caps are typically not reverse thread. Most hydraulic cylinder caps have a standard thread direction, and removing them is similar to removing any other threaded component. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the correct tools when removing and reinstalling caps.
To calculate the force generated by a hydraulic cylinder, you need to know the cylinder bore diameter, the operating pressure, and the piston rod diameter. The formula for calculating hydraulic cylinder force is:
Force (in pounds) = (Pressure (in psi) x Cylinder bore area (in square inches)) – (Pressure (in psi) x Piston rod area (in square inches))
By knowing the force generated by the hydraulic cylinder, you can select the appropriate size and capacity for your application.
Learn more about hydraulic power from the Encyclopedia Britannica.
Step 1: Gather Tools and Safety Gear Before you start, ensure you have the necessary tools and safety gear. You’ll likely need wrenches, a rubber mallet, safety glasses, and gloves.
Step 2: Depressurize the System Safety first! Release the hydraulic pressure by disconnecting any power sources and operating the cylinder to release any remaining pressure. This prevents unexpected movements during disassembly.
Step 3: Locate the Retaining Bolts Identify the bolts that hold the end cap in place. They’re typically positioned around the circumference of the end cap.
Step 4: Loosen the Bolts Using the appropriate wrench, carefully loosen the retaining bolts. Start by loosening them evenly to avoid putting stress on one side of the end cap.
Step 5: Tap the End Cap Gently tap the end cap with a rubber mallet. This helps break any seal that might have formed due to pressure and fluid.
Step 6: Remove the Bolts and End Cap Fully remove the retaining bolts and gently slide the end cap away from the cylinder body. Be prepared for a slight release of hydraulic fluid as you do this.
Step 7: Inspect and Clean With the end cap removed, inspect the interior for any signs of damage or wear. Clean the sealing surfaces and ensure no debris could affect reassembly.
Step 8: Replace or Maintain Depending on the reason for removal, this is the time to either replace a damaged part or perform any necessary maintenance.
Step 9: Reassembly When you’re ready to put everything back together, reverse the steps. Carefully position the end cap back onto the cylinder body, making sure the seal is properly aligned. Reattach and tighten the retaining bolts evenly.
Step 10: Test and Check for Leaks After reassembly, re-pressurize the system and test the cylinder’s operation. Keep an eye out for any hydraulic fluid leaks around the end cap area.
Remember, safety is paramount. If you’re unsure at any point or encounter difficulties, it’s always a good idea to consult a professional or refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines. With patience and attention to detail, you can successfully remove a hydraulic cylinder end cap and carry out necessary repairs or maintenance.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, hydraulic cylinders are an essential component of hydraulic systems, and understanding their mechanics, materials, and maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By addressing common issues such as drift, airlock, and proper sizing, you can prevent damage to the system and extend the life of your cylinders. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and seek the assistance of a qualified technician for repairs and maintenance. With proper care and maintenance, hydraulic cylinders can provide reliable performance and power for years to come.